Frequently Asked Questions
With all this talk of Aquaponics and the lost methods of living reliantly relatively new to everyone – there is a need to have a place of reference for the terms you will be coming across. By no means is this a full treatise on the verbal lexicon of it all but it is a good stab at most of them here below – take a look.
Active Principle: A plant chemical proven to have a medical effect.
Antiseptic: A substance that prevents or stops the growth of microorganisms that cause infection.
Astringent: A substance the draws together the soft tissues such as skin or mucous membranes.
Decoction: A drink or liquid extract made by boiling plant bark, roots, berries, or seeds in water.
Diuretic: A substance that increases the flow of urine.
Emollient: A substance that softens and soothes the skin and mucous membranes.
Essential Oil: A plant oil that vaporizes readily and is often obtained by steam distillation.
Expectorant: A substance that loosens and helps to expel phlegm.
Herbal Tea: A beverage made from steeping or boiling herbs.
Infusion: A preparation in which flowers, leaves, or stems are steeped in water that is not boiling.
Liquid extract: Concentrated infusion made by soaking an herb in distilled water, grain alcohol, or glycerin for a long period.
Mucous membrane: Lining of the body passage, such as the throat, that protects itself with secretions of mucus.
Photosensitivity: Sensitivity to sunlight, resulting in a rash or burning sensation, brought on by ingestion or application of certain substances.
Plaster: Gauze or cloth in which medicine has been wrapped. Plaster is typically applied to the skin.
Poultice: An herbal preparation that is usually applied directly to the affected area to relieve pain or swelling.
Purgative: A very strong laxative.
Tannins: Astringent and bitter compounds found in the seeds and skins of grapes, which slow oxidation and aging.
Tincture: An herbal liquid extract that generally involves macerating the herb in alcohol.
Volatile Oil: A plant oil that vaporizes readily and is often obtained by steam distillation, used interchangeably with essential oil.
Wash: A liquid herbal medicine preparation for external use.
Connecting Piping in Your System – You can use a silicon based glue, but keep in mind you will need to get the Aquarium Safe version as well have patience to let it cure. The better way to do this is to drill your hole slightly smaller than your fitting, heat the rim of that hole up a wee bit with a welding torch and screw the threaded male fitting through the warmed hole~ no silicone is needed when you get a nice tight fit. Practice on the top of the bed for an overflow hole if need be.
Helping the pH Balance Adjust – Calcium Carbonate or Potassium BiCarbonate are the two primary buffering products to use and both readily available at the local Home Depot or Lowes. Calcium Carbonate is available for rural supply shops horse suppliers etc. Shell grit will do just as well although more a slow release buffer over time. Some people use “slaked lime” and or “hydrated lime” Calcium Hydroxide which breaks into Calcium Carbonate in the presence of Carbon Dioxide. Gypsum can be used to adjust the “hardness” (a measure of Ca/Mg) of your water lemons, vinegar and Hydrochloric acid can be used to move pH in the other direction…. use with care and caution… and very discretely…. 1ml in 1000l will move your pH by 0.1….
Pump Size for System – The purpose of moving the volume of water through the grow beds is to allow the bacteria to work. There are other reasons such as solids removal and oxygenation, but that is secondary. If you have a 1000 litre fish tank, operating on the 45minOFF/15minON then you will need a 4000lph pump as a minimum assuming minimal head.
Blue drum – 200L plastic drum used in many areas of aquaponics. Can be cut in half vertically or horizontally to give two 100L grow beds. Care needs to be taken when obtaining these drums that toxic chemicals have not been stored in them. Depending on the previous use of the drum, they may be successfully cleaned and used in your system.
Crenellations – cover a greater surface area compared to a series of drilled holes and thus lets a greater water flow through, holes are more prone to clog. Think of the tops of medieval castles _|-|_|-|
Fish-safe silicone– (from a supplier) a medium modulus, one component, acetic cure silicone recommended specifically for the fabrication and repair of fresh or salt water aquariums. It forms a tough waterproof seal that won’t crack or shrink and is non-toxic to fish when fully cured after 7 to 14 days. Cure time depends on bead size and cure conditions.
Does not contain fungicides that will kill your fish.
Float switch – an electrical switch used to turn pumps on and off during pumping cycles. The usual configuration in aquaponics has the Switch switching ON when the float is in the UP position…. The switch switches the pump ON when the tank is full and then the pump being switched on will pump to empty the tank. When the float is DOWN, the pump switches OFF.
IBC– Industrial / Intermediate / International Bulk Carriers, 1000L, usually 1000mm x 1000mm x 1000mm (approx.) plastic cubes used to transport bulk liquids by road or rail. They are usually white / translucent and contained within a steel or aluminum cage on a pallet. Care needs to be taken when obtaining these ibc’s that toxic chemicals have not been stored in them. Specialist fittings are often required to couple to the tap in the bottom of the ibc.
Plastic types – some different types of plastic and other pipes and their usages
PVC Pipe
- PVC stands for Polyvinyl Chloride.
- Used for carrying cold water, irrigation, as a conduit and for DWV (drain-waste-vent) projects.
- Rated by thickness and strength. Common ratings (thickest to thinnest) are Schedule 40 (most common), Class 315, Class 200 and Class 125 (generally used for irrigation).
- Available in sizes from 1/2” to 2”. White in color
CPVC Pipe
- CPVC stands for Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride.
- Used for both hot and cold water supply or chemical distribution systems.
• Good for temperatures at 200° F in pressure systems and non-pressure systems.
• Requires special solvent cement that is different from cement used for other types of plastic solvents. Most solvents will indicate this on the can.
ABS Pipe
- Means Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene.
- Made from a thermoplastic resin. Lightweight and easier to use than metal pipe.
- Commonly used for DWV (drain-waste-vent) applications or for underground electrical conduits.
- Available as either solid wall or cellular core construction
Black Poly Pipe
- Used for carrying low-pressure cold water. Common applications include golf course sprinklers, underground conduits or to carry corrosive liquids and gases.
- Good chemical and crush resistance.
- Lightweight enough to cut with an ordinary knife or a fine-toothed hacksaw blade.
PEX Pipe
- PEX stands for cross linked polyethylene.
- The chief advantage is its flexibility and strength. It can make turns around corners without couplings.
- In a PEX plumbing system, a separate line is run from the main water supply to each fixture in a set up much like a circuit breaker box.
- Used for carrying hot and cold water.
- Excellent chemical resistance to acids and alkalis, but do not use for fuel oil, gasoline or kerosene systems.
- Do not weld with solvents. Join with heat fusion, flare, crimp ring or compression fittings.
Galvanized Pipe
- Has zinc coating that prevents rust if not scratched.
- Use primarily for carrying water or waste. Do not use for gas or steam.
- Common water sizes are 3/8”, 1/2”, 3/4” and 1”. Common waste sizes are 1-1/2”, 2” and 3”.
- Often sold in pre-threaded standard lengths, or can be custom threaded.
- Use only with similar galvanized pipe fittings, not with black pipe fittings.
- Measured using the I.D. (inside diameter)
Black Iron Pipe
- Not treated for rust resistance.
- Used for carrying steam or gas.
- Used only with black iron pipe fittings, not galvanized fittings.
- Measured using the I.D. (inside diameter).
Water Supply Tube
- Used to connect a water supply line to a faucet fixture, toilet or appliances. Several types available.
- Plastic type is flexible and inexpensive but not designed for exposed connections.
- Ribbed chrome type bends easily without kinking.
- Braided type features pre-attached connector nuts at both ends and can be flexed to fit.
- Chrome-plated copper or brass tubes are more rigid than other types and are good for exposed applications.
- The most common size is 3/8″, with lengths ranging from 6″ to 72″.
Vinyl Tubing
- Economical and used in a variety of applications.
- Usually joined with pressure fittings and clamps
Plastic Recognition By Burning
Plastics recognition – plastic type – Observations when lit with match and allowed to burn
PVC – Blackish smoke and acrid smell
Polyethylene – No smoke, drips like a candle and smells of wax
Polypropylene – No smoke, drips like a candle and smells of burnt oil
Polyamide – No smoke, pulls to form a thread, smells of burnt horn
Polycarbonate – Yellowish sooty smoke, sweetish smell
ABS – Blackish smoke, soot flakes, sweetish smell
Plumbing sizes / grades – PVC pipes come in pressure and DWV (Drain Waste Vent) grades. These are NOT the same thing. They are NOT the same size. Make sure before you buy the fittings and pipes that you get the same type of fittings. They will not match up easily and mixing them up can make for hassles and dodgy joins and unwanted expense.
Poly pipes come in pressure and rural grades. Again, these are NOT the same thing or size.
There are mainly differences in the thickness of the pipes and the strength of the joiners required to hold the pipes together.
Pumping head– Expression of pressure in height of water. The height of one body of water above another at the first place where it is open to the atmosphere. For example, if the water is piped from a lake in the hills down to a farm in the valley and the surface of the lake is 100m above the surface of the fish ponds, the water has a head of 100m at the level of the fish ponds. If however, the pipe is stopped halfway, the water allowed to form another lake and then piped the rest of the way, the head at the fish tanks will only be 50m see also friction loss for calculations for air and water loss in pipes.
Many pumps will state, for example, 10m maximum head. This means if you are pumping to 10m high, you will deliver 0L water per hour (not much use to anyone really). But the same pump, pumping to 4m high, will deliver about 200L (all figures examples only)
Sump – General term for a tank or chamber used as a reservoir, stilling chamber or water collection point.
Timer – often used to regulate flood and drain cycles. Varying on / off cycles available. Also, varying degrees of program ability.
Hygrometer – An instrument for measuring relative humidity in the atmosphere.
Media-Based Aquaponics – Where the filtration (both bio and solids) takes place in the media (inert plant growing material such as a gravel or other aggregate) within the grow bed. The water delivery can be constant-flow, timed or flood and drain. The functions of a media bed are:
1-a media bed supports the plants
2-a media bed provides solids filtration
3-a media bed provides bio-filtration
4-a media bed provides a home for worms
NFT (Nutrient Film Technique) – A method of growing plants in which a thin and even film of aerated nutrient solution flows down a channel into which the roots of the crop are suspended. It is very important to filter the water well before sending it to an NFT trough since fish waste in the trough and on the plant roots will negatively impact the plant’s growth. NFT aquaponics requires separate solids and bio-filtration. While the reduced amount of water needed to fill the system may seem like a benefit, it can mean greater temperature and water quality fluctuations in a short period of time.
DWC (Deep Water Culture) – DWC is often referred to as Raft where the plants grow suspended over a tank of water in which nutrient-rich water flows with supplemental aeration. In most situations, filtration needs to occur before fish water is sent to the raft area of the system.
CHIFT PIST (Constant Height In Fish Tank Pump In Sump Tank) – Maintaining a constant volume/height in the fish tank with a sump tank at the lowest point and a fish tank at a higher point. The pump lifts water from the sump tank to the fish tank and water flows from the fish tank to the grow beds which drain back to the sump tank.
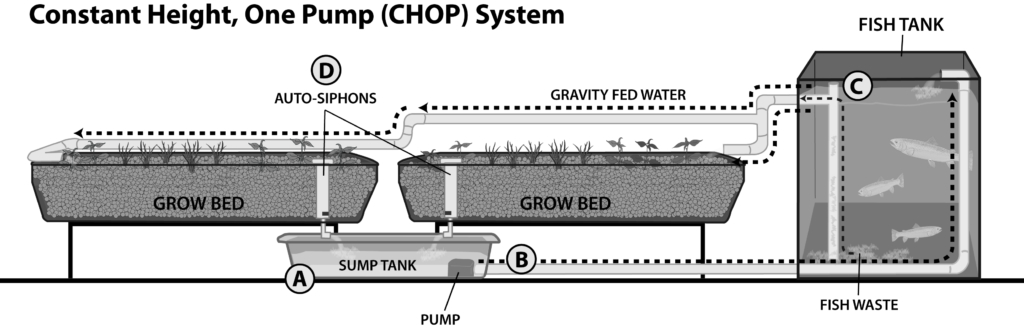 CHOP (Constant Height One Pump) – Basically the same thing as CHIFT PIST. With CHIFT PIST there has not normally been a distinction between the variation where the fish tank drains back to the sump directly and the pump pumps to the grow beds and they might drain to the sump or the fish tank. With CHOP it was normally assumed that the fish tank got the water from the pump and drained to grow beds which drained to the sump.
CHOP (Constant Height One Pump) – Basically the same thing as CHIFT PIST. With CHIFT PIST there has not normally been a distinction between the variation where the fish tank drains back to the sump directly and the pump pumps to the grow beds and they might drain to the sump or the fish tank. With CHOP it was normally assumed that the fish tank got the water from the pump and drained to grow beds which drained to the sump.
CHOP2 – The variation of CHIFT PIST where both the fish tank and grow beds drained to the sump and the sump pumped to both the grow beds and fish tank
Constant Flow – Same as the Simple Flood and Drain, except when you remove the timer, the system is constantly flooding
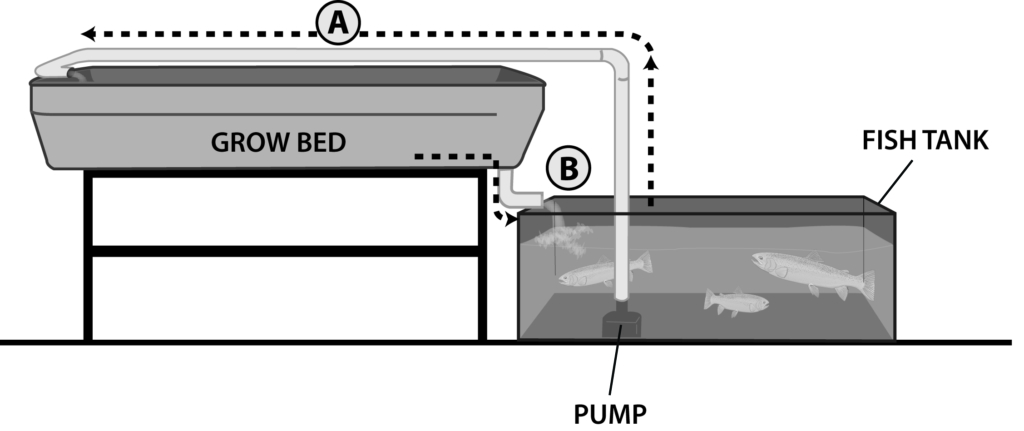 Flood and Drain– The plant growing space is allowed to flood and then drain either by the use of a pump on a timer to fill the bed and then allow it to drain while the pump is off or by the use of a siphon or other intermittent outflow device where the bed is constantly filling and then the siphon will drain the bed quickly.
Flood and Drain– The plant growing space is allowed to flood and then drain either by the use of a pump on a timer to fill the bed and then allow it to drain while the pump is off or by the use of a siphon or other intermittent outflow device where the bed is constantly filling and then the siphon will drain the bed quickly.
Advantages: providing ample oxygen to plant roots and bio filter bacteria without the need of extra aeration. Many plants like some dry time especially if the water is not super aerated.
Disadvantages: Water level needs to fluctuate in the system to provide the water for flood and drain. Flood and drain offers more media to air than media to water interface which can have an exaggerated heat exchange effect on water temperatures.
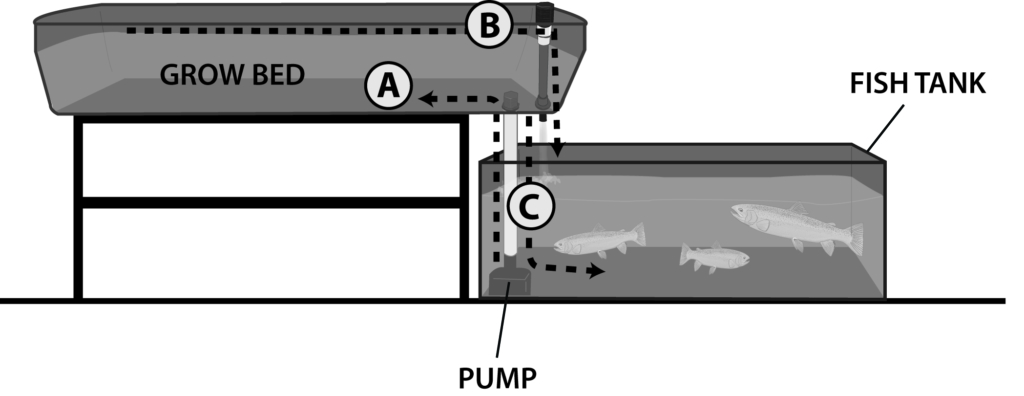 Ebb and Flow – The same as Flood and Drain except you are usually pumping up through the bottom of the grow bed and then when the pump turns off, you are draining back down through the pump.
Ebb and Flow – The same as Flood and Drain except you are usually pumping up through the bottom of the grow bed and then when the pump turns off, you are draining back down through the pump.
IPPM – integrated production and pest management
Barramundi – A fish for warm climates, can be also used as the summer choice in locations that don’t have high temperatures year long. If barramundi will be your fish for the summer in your area then you should buy mature stock for your system so you will be able to harvest your fish by the end of the season. Barramundi will give you a very clean taste.
Catfish – There are many different species of catfish around the world and many of them grow up good as aquaponics fish. The channel catfish is the one that we find in fish farming in the United States and in many places in Australia. Catfish has to be skinned in order to be cooked and has a very nice taste.
Tilapia – This fish species is native in Africa and ancient Egyptians were farming it 4000 years ago. Tilapia loves the warm climates and it is the number one choice for farmers that live in locations that can provide them. Tilapia is the most popular Aquaponics fish
Trout – Rainbow and Brown – An aquaponics fish for cold water only. This fish with the majestic taste is the best choice throughout the year for growers that live in cold climate locations or for winter months only in places that also have warm seasons. Trout is a fish with high demands and needs pristine water conditions in order to grow up good. We have to know that if we choose trout to grow it in our system we will have some limitations in the selection of the plants we will farm in our grow beds, because most of the aquaponic farming plants like warmer water temperatures.
White Bass – This fish, along with its delicious taste can be an excellent choice for your tank. It likes to eat small crabs and fish. White bass is laying hundreds of thousands of eggs during the spawning season. The size of this fish is 9 inches long on average.
Crappie – One of the best fish species for your AP Crappies develop really well in the closed system of aquaponics tank and taste delicious as well. They have to become two years old in order to mate and reproduce; and this can be considered a disadvantage, but it is definitely something to consider. Crappies are carnivorous and like to eat crabs and small insects. Never stock your crappies with bigger fish because they will end up being fish food!!
Koi – Another ornamental species that will thrive in the environment of aquaponics system because it is used to living in large ponds. Both Coi and Goldfish can be sold at pet shops if their growers wish so.
Goldfish – For the growers that don’t like to eat fish this ornamental species can be a secure choice. Goldfishes can stand even the hardest water conditions. Goldfishes are tropical water fishes and so they like the hot climates. If we want them to breed we have to add to our tank some plant cover.
GH – General hardness (a measure of the concentration of divalent metal ions such as calcium Ca2+, and magnesium Mg2+)
KH – Carbonate hardness (a measure of the alkalinity)
pH – “power/potential of hydrogen” (A measure of the concentration of Hydrogen atoms, H+)
Alkalinity – The capacity of water for neutralizing an acid
Acid – The negative logarithm of the concentration of hydronium ions – substance that increases the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) in solution
Base – The positive logarithm of the concentration of hydronium ions –
substance
that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate a pair of valence electrons. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions (OH−)
Ion – An atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons
Anions – Negatively charged ions
Cations – Positively charged ions
Chelate – The way ions and molecules bind metal ions to allow the metals to be available to plants as nutrients
Ligand – That which binds to a central metal atom
Divalent – Forming two bonds with other ions or molecules
Anhydrous – Contains no water
AOB – ammonia-oxidizing bacteria
C:N – carbon and nitrogen ratio
CaO – calcium oxide
CaOH2 – Calcium hydroxide (also called slaked lime, hydrated lime, pickling lime, builders lime)
CaCO3 – Calcium carbonate (Chalk, agricultural lime)
CO2 – carbon dioxide
CO3 2– carbonate
C – Carbon
Ca – Calcium
Cl – Chlorine
Cu – Copper
CP – crude protein
DE – digestible energy
DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid
DO – dissolved oxygen
DWC – deep water culture
EAA – essential amino acids
EC – electrical conductivity
EFA – essential fatty acids
Fe – Iron
FCR – feed conversion ratio
GAP – good agricultural practice
H+ – hydrogen ion
H2CO3 – carbonic acid (formed by CO2 and H2O as in club soda, soda water, sparkling water, or seltzer water and acid oceans due to burning fossil fuels)
H2S – hydrogen sulphide
H2SO4 – sulphuric acid (Used in acidic drain cleaner, and electrolyte in lead-acid batteries)
H3PO4 – phosphoric acid
HCl – Hydrogen Chloride (forms Hydrochloric acid the aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride)
HCO3 – bicarbonate
HNO3 – nitric acid
K – Potassium
K2CO3 – Potassium carbonate. (primary component of potash)
K2SO4 – Potassium sulfate
KCl – Potassium chloride (available as water softener)
KHCO3 – Potassium bicarbonate (an ingredient of baking powder, also used in fire extinguishers)
KOH – potassium hydroxide
LDPE – low-density polyethylene
LECA – light expanded clay aggregate
Mg – Magnesium
Mn – Manganese
NaCl – sodium chloride
N – nitrogen
Ni – nickel
N2 -molecular nitrogen
NFE – nitrogen-free extract
NaHCO3 – Sodium bicarbonate (Baking soda)
NH3 – ammonia
NH4 + – ammonium
NHO3 – nitric acid
NO2 – – nitrite
NO 3 – nitrate
NOB – nitrite-oxidizing bacteria
OH – Hydroxide (functions as a base)
μS/cm – microSiemens per centimetre
ppm – parts per million
ppt – parts per thousand
PVC – polyvinyl chloride
SSA – specific surface area
TAN – total ammonia nitrogen
TDS – total dissolved solids
UV – ultraviolet
Abscission: The dropping of leaves, flowers, or fruit by a plant. This can result from natural growth processes (e.g., fruit ripening) or from external factors such as temperature or chemicals.
Abscission Layer: Specialized cells, usually at the base of a leaf stalk or fruit stem, that trigger both the separation of the leaf or fruit and the development of scar tissue to protect the plant.
Absorption: The intake of water and other materials through root or leaf cells.
Adventitious: Growth not ordinarily expected, usually the result of stress or injury. A plant’s normal growth comes from meristematic tissue, but adventitious growth comes from nonmeristematic tissue.
After-ripening: The seed maturation process that must be completed before germination can occur.
Algae: is an informal term for a large, diverse group of photosynthetic organisms which are not necessarily closely related and are thus polyphyletic
Algal Bloom: A rapid growth of microscopic algae or cyanobacteria in water, often resulting in a colored scum on the surface.
Allelopathic: An allelopathic plant is one that secretes and/or broadcasts chemical compounds that are actively inhibitive to the growth of plants around it. Look under any redwood tree: you will find very little weed growth among the redwood needles because they are allelopathic. An example in aquaponics systems is tomatoes. If any other plant’s roots are touching or nearby a tomato’s roots (except basil, which doesn’t seem to mind), the other plant will do poorly and perhaps even die from the contact.
Apex: The tip of a stem or root.
Apical bud: A bud at the tip of a stem.
Apical dominance: The inhibition of lateral bud growth by the presence of the hormone auxin in a plant’s terminal bud. Removing the growing tip removes auxin and promotes lateral bud break and subsequent branching, usually directly below the cut.
Apical meristem: A region of actively dividing cells at the tip of a growing stem or root.
Attenuate: When a plant grows tall and spindly instead of “bushing out” as it normally would; this is an indication the plant is not getting enough light, and/or is planted too densely.
Autotrophic nutrition: A form of nutrition in which complex food molecules are produced by photosynthesis from carbon dioxide, water, and minerals
Buffering action: The ability of a nutrient solution or raw water to resist changes in pH
Chlorosis: An abnormal yellowing of a leaf.
Clay: The smallest type of soil particle (less than 0.002 mm in diameter).
Cole Crops: A group of vegetables belonging to the cabbage family; plants of the genus Brassica, including cauliflower, broccoli, cabbage, turnips, and brussels sprouts.
Electrical Conductivity (EC): A measure of the ability of a nutrient solution to conduct electricity, which is dependent upon the ion concentration and nature of the elements present. Visit our selection of solution testing equipment.
Green Leaf Vegetables: Chinese cabbage, lettuce, basil, spinach, chives, herbs and watercress
Fruiting Plants: Cucumbers, tomatoes, capsicum, red onions, string beans, peas, melons, squash
Tuberous Root Plants: ginger, turmeric, ginseng, radishes, carrots, potatoes, turnips, beets, and yams
Growing Medium: Materials that are sometimes used in hydroponic growing to support the plant’s roots and, sometimes, to hold nutrient.
Hardening Off: The process or gradually exposing seedlings started indoors to outdoor conditions before transplanting.
Necrosis: Tissue death, browning of leaf tissue due to a nutritional disorder.
N-P-K: The acronym for the three primary nutrients contained in manure, compost, and fertilizers. The N stands for nitrogen, the P stands for phosphorus, and the K stands for potassium. On a fertilizer label, the N-P-K numbers refer to the percentage of the primary nutrients (by weight) in the fertilizer. For example, a 5-10-5 fertilizer contains 5% nitrogen, 10% phosphorous, and 5% potassium.
Seed Coat: A hard outer covering that protects a seed from disease and insects. Also prevents water from entering the seed and initiating germination before the proper time.
Seedling: A young plant, shortly after germination.
Senescence: (1) The aging process. (2) A descriptive term for a plant that is in the process of going dormant for the season, although technically only the parts that are dying (the leaves) are becoming senescent.
Thermoperiod: The change in temperature from day to night.
